The Solar Radiation Sensor Working Principle
The Solar Radiation Sensor Working Principle
Introduction
Understanding the working principle of solar radiation sensors is as difficult as knowing the secrets of the sun. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explain the intricate details about the operation of these sensors, giving you a deeper insight into the fascinating world of solar technology.
The Essence of Solar Radiation
Solar radiation is the lifeblood of solar energy systems. It is the radiant energy emitted by the sun, consisting of various wavelengths. To use this energy efficiently, we need to understand the fundamental principles governing solar radiation sensors.
The Basics of Solar Radiation Sensors
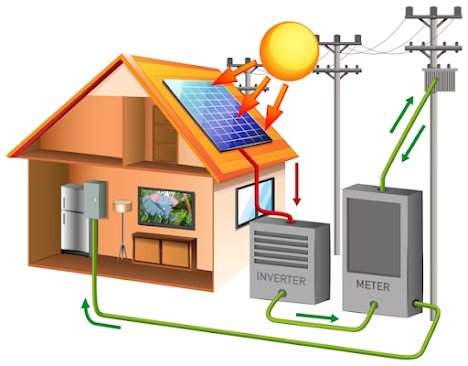
Sensing the sun's rays
Solar radiation sensors, often called solar radiation sensors, are devices that measure the intensity of solar radiation. They work on the principle of the photovoltaic or photoelectric effect, where sunlight striking a surface produces an electric current.
Photovoltaic Effect Unveiled
The photovoltaic effect is a phenomenon where certain materials produce an electric current when exposed to light. In the case of solar radiation sensors, this effect is used to convert sunlight into measurable electrical signals.
Components and Operation
Photodiodes: The Heart of the Sensor
At the core of every solar radiation sensor is a photodiode. It is a semiconductor device that converts photons coming from sunlight into electrons, thereby generating an electric current proportional to the intensity of light.
Circuitry and Signal Processing
The generated electric current is then processed through sophisticated circuitry within the sensor. This circuitry refines the signal, filtering out noise and providing a precise measurement of solar radiation intensity.
Types of Solar Radiation Sensors
Pyranometers: Measuring Total Solar Radiation
Pyranometers are the workhorses of solar radiation measurement, capturing the total solar radiation across all wavelengths. They consist of a thermopile or photodiode that produces an output voltage proportional to the incoming solar radiation.
Pyrheliometers: Focusing on Direct Solar Radiation
Pyrheliometers take into account the position of the sun and specialise in measuring direct solar radiation. They contain a collimator that directs sunlight onto the thermopile, providing accurate readings of direct solar radiation.
Applications and Impact
Solar energy optimisation
Solar radiation sensors play a pivotal role in optimising solar energy systems. By providing real-time data on solar radiation levels, these sensors enable solar panels to adjust their orientation and maximise energy harvest.
Meteorological Insights
Beyond their energy applications, solar radiation sensors also contribute to meteorological research. They help us understand climate patterns, providing important data for weather forecasting and environmental monitoring.
Advancements and Future Trends
Integration with the IoT and AI
The future of solar radiation sensors lies in their integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. This synergy allows for more sophisticated data analysis, predictive modelling, and enhanced energy optimisation.
Miniaturisation and Wearable Tech
As technology progresses, we anticipate the miniaturisation of solar radiation sensors, paving the way for wearable devices. Imagine a world where personal gadgets can harness solar energy, driven by sensors embedded seamlessly into clothing or accessories.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the solar radiation sensor's working principle is an intricate dance between photons, semiconductors, and electric currents. As we unlock the secrets of the sun, we pave the way for a future where solar technology seamlessly integrates into our daily lives, shaping a more sustainable and energy-efficient world.
Comments
Post a Comment